
by First Integrity Team Supreme Lending | Mar 20, 2025
Deciding between renting vs. owning a home may be one of the biggest debates when it comes to housing. Both options offer unique advantages, but the key is to find which fits your personal goals and lifestyle. Let’s explore the pros and cons of each option and take a deep dive into the many potential benefits of homeownership and mortgage options that renters may not realize.
Pros and Cons of Renting
Renting offers flexibility and lower upfront costs, making it an appealing option for many. Here are some of the possible benefits and drawbacks of renting.
Pros of Renting
- Renting allows you to move more easily, ideal for those who frequently relocate or prefer not to be tied down to one area.
- Less Responsibility. When renting, your landlord or property management company is typically responsible for maintenance, repairs, and property upkeep. This saves you the headache of managing those tasks and additional costs.
- Lower Upfront Costs. When moving into a new rental, security deposits and first month’s rent are typically more affordable than a down payment for a home and other homebuying costs.
Cons of Renting
- No Home Equity. Making rent payments doesn’t build equity—unlike the potential for a home. No equity means you can’t take advantage of opportunities like cashing out on equity with a refinance.*
- Limited Personalization. Rental properties often have restrictions on renovations or even simple changes like painting walls and installing new fixtures.
- Rising Rents. Unlike a fixed mortgage, rent payments can oftentimes increase every year, sometimes significantly depending on your local market conditions.
Benefits of Owning
While renting may offer short-term convenience, owning a home comes with several potential long-term benefits that renting can’t match. Beyond simply having a place to live, explore these rewards of homeownership:
- Potential to Build Equity. Home values may appreciate over time. Unlike renting, homeownership may allow you to build equity as a future investment.
- Stable Payments. With fixed-rate mortgages, you have the confidence and peace of mind that your monthly payments will remain the same throughout the life of the loan.
- When you own your home, you have the creative freedom to really make it your own. You can make as many home renovations as you want to fit your unique style.
- Possible Tax Benefits. Homebuyers may qualify for potential tax deductions. Work with your tax advisor to learn more and see if owning a home could save you tax dollars.
- Pride of Ownership. There’s a unique sense of accomplishment and pride that comes with owning a home, allowing you to put down roots in a community.
Renting vs. Buying: Seven Key Questions to Consider
- How long do you plan to stay in one place? If you’re planning to stay in one location for several years, buying may be a smarter option.
- What’s your financial situation? Do you have enough savings for a down payment and closing costs? Evaluate your finances and get pre-qualified to determine your options.
- Are you ready for the responsibilities of homeownership? Owning a home comes with additional responsibilities than renting such as on-going maintenance, repairs, and upkeep.
- What’s your credit score? Your credit score plays a significant role in qualifying for a mortgage and getting favorable loan terms.
- What are the housing market trends in your desired area? Depending on your local area, it may make more sense to rent if housing prices are too high or out of your budget.
- Do you value flexibility or stability more? Consider your current lifestyle preferences. If you’re not ready to settle down, renting may offer the flexibility you need. However, if you’re drawn to a more stable living situation, homeownership may be the better option.
- What are your long-term goals? How could homeownership fit in with your broader financial and lifestyle goals, such as the potential to building equity, undergoing home renovations, investing in real estate, or creating a family home.
Down Payment Assistance & First-time Homebuyers
Don’t forgot to explore down payment assistance and first-time homebuyer programs that may help open the door to homeownership sooner than you think! FHA loans offer several benefits for first-time buyers, including lower down payment and credit requirements. While Conventional loans may only require as low as 3% down for qualified first-time buyers.
Ready to Stop Paying Your Landlord’s Mortgage?
Deciding between renting vs. owning a home is a big decision that depends on several factors such as your mortgage qualification, long-term plans, and personal preferences. While renting offers flexibility, homeownership may offer long-lasting benefits.
Ready to explore your homebuying options? Contact our team at Supreme Lending to discuss how to make your mortgage work for you!
*By refinancing an existing loan, total finance charges may be higher over the life of the loan.
by SupremeLending | Jul 29, 2024

If you’re thinking of buying a home, you may want to consider the possibility of seller concessions to help reduce upfront loan expenses. Imagine having a portion of your mortgage closing costs covered or even getting some essential home repairs taken care of without having to dig into your savings. That’s where seller concessions come in, also known as seller assistance. It can be a significant benefit for both buyers and sellers. In this guide, we’ll explore what seller concessions are, seller assist limits, and frequently asked questions.
What Are Seller Concessions?
Seller concessions are contributions paid by the seller that go toward the homebuyer’s closing costs. These can include closing fees, prepaid expenses, or even home repairs or improvements. These concessions can help lower the amount of money a buyer needs to bring to the closing table, making the home purchase more affordable.
The concession amount can be expressed as a percentage of the home’s purchase price or fixed dollar amount.
Examples of What Seller Concessions Can Cover
Seller concessions can be used for a variety of mortgage and homebuying costs including:
- Loan Origination Fees. Fees charged by the lender for processing the loan application.
- Appraisal Fees. This is the cost of having a home appraised.
- Home Inspection Fees. This is the cost of having a home inspected before closing.
- Property Taxes. Prepaid property taxes may be included in closing.
- Title Insurance. This insurance protects the buyer and lender from potential disputes over ownership.
- Discount Points. Also known as mortgage points, these help pay down the interest rate using upfront costs.
- Home Repairs or Improvements. Costs for necessary repairs identified during the home inspection or agreed-upon improvements before the sale.
How Do They Work?
- Negotiation. Seller concessions are typically negotiated as part of the buyer’s and seller’s purchase agreement. This request can be made with help from a real estate agent.
- Agreement. If the seller agrees to concessions, the specific details are outlined in the contract and must not exceed a specified limit depending on the loan type.
- Appraisal. The agreed-upon concessions cannot inflate the property’s value. Lenders require an appraisal to ensure the property’s market value supports the loan amount, including the concessions.
- Loan Approval. The lender will review the agreement and appraisal. This will ensure that the concessions align with the mortgage program’s guidelines.
- Closing. When the loan is ready to close, the costs are applied to the buyer’s closing costs or other agreed-upon expenses.
Who Benefits from Seller Concessions?
Both the buyers and sellers can benefit!
- Buyers. Concessions can lower the upfront costs needed to buy the home, making it easier to afford the property.
- Sellers. Offering concessions can also make the home more attractive for potential buyers, helping sell the home quicker.
Seller Assistance Limits
Limits on how much a seller can contribute vary depending on the loan type and down payment:
Conventional Loans
- Primary residence and second homes:
- 3% maximum with less than 10% down
- 6% maximum with 10-25% down
- 9% maximum with more than 25% down
- Investment properties:
- 2% maximum regardless of down payment
FHA/USDA Loans
- 6% maximum toward closing costs and prepaid items
VA Loans
- 4% maximum toward prepaid items
- No limit for closing costs or reasonable discount points
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the seller cover the entire down payment?
No. Seller concessions cannot be used for the full down payment. They are typically used for closing costs, prepaid expenses, and other associated fees, while meeting the loan guideline limits.
Does seller assistance affect the loan approval process?
Seller concessions themselves do not affect loan approval, but lenders can consider the impact on the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio and may require specific guidelines.
How does it impact the home appraisal?
The home’s appraisal must support the purchase price, including any seller contributions. If the appraised value is lower than the agreed-upon price, the lender may require adjustments.
Can a buyer negotiate for concessions?
Yes! Homebuyers can request this during negotiations. It’s essential to work with a knowledgeable real estate agent to help navigate the process.
How do seller concessions benefit first-time homebuyers?
First-time buyers often benefit from this as they may have limited funds for closing costs and other expenses. Seller assistance is another great way for more people to unlock the door to homeownership!
If you’re ready to start your homebuying journey, your local Supreme Lending team is ready to help! Contact us to learn about your mortgage options and get pre-qualified today.
by SupremeLending | Jul 18, 2024
When it comes to securing a mortgage, a key factor that lenders consider when evaluating a borrower’s lending capacity is Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio. Understanding mortgage LTV, how it’s calculated, and how it can impact your mortgage can help you make informed decisions during the homebuying process. Let’s dive into the details of LTV ratios and why they matter.
What Is Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio?
The LTV ratio is a financial term used by lenders to assess the risk of a loan. It compares the loan amount to the appraised value of the property being purchased or refinanced.* The LTV ratio is expressed as a percentage, demonstrating how much of the property’s value is being financed through the mortgage.
*By refinancing an existing loan, total finance charges may be higher over the life of the loan.
How Is Mortgage LTV Calculated?
The LTV ratio is calculated using the following formula:
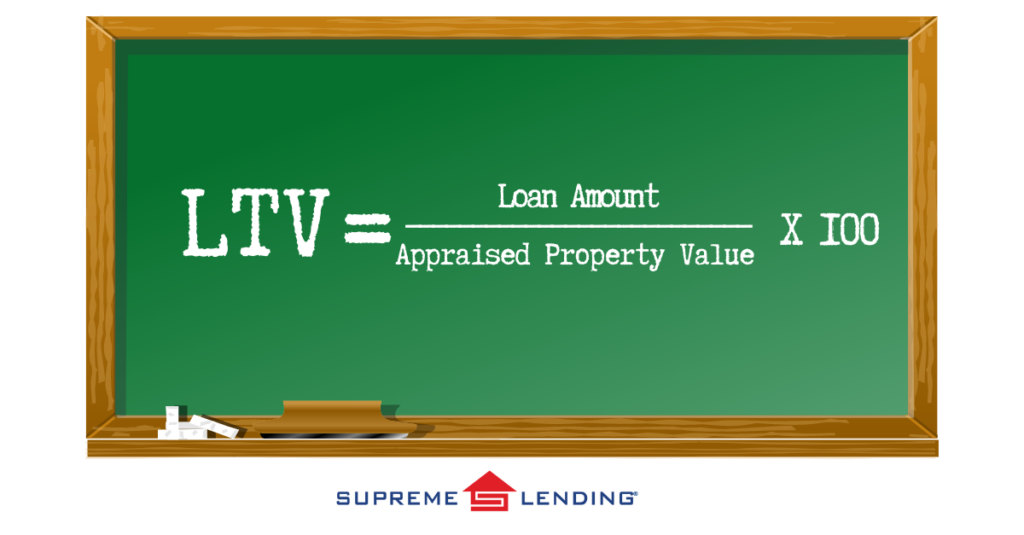
For example, if you’re purchasing a home with an appraised value of $300,000, and you’re borrowing $240,000, the mortgage LTV would be 80%:

How LTV Relates to Mortgage and Homebuying
LTV ratios play a crucial role in the mortgage approval process. Lenders use LTV to determine the level of risk associated with a loan. A lower LTV signifies lower risk, as the borrower has more equity in the property. Consequently, a higher LTV indicates higher risk for the lender, as the borrower has less equity.
How to Measure Mortgage LTV Ratios
A fair LTV ratio is typically 80% or lower. An LTV ratio of 80% or less is favorable because it often means the borrower is not required to pay for private mortgage insurance (PMI), which is usually mandatory for higher LTV ratios. PMI protects the lender in case of default but adds extra cost for the borrower.
LTV Requirements by Common Loan Types
Loan-to-Value criteria depends on the type of loan. Here’s a breakdown of common LTV limits to keep in mind:
- Conventional Loans:
- Maximum LTV: 80% to avoid PMI
- With PMI: Up to 97%
- FHA Loans:
- Maximum LTV: 96.5% for borrowers with a credit score of 580+
- VA Loans:
- Maximum LTV: 100% (no down payment required for eligible Veterans)
- USDA Loans:
- Maximum LTV: 100% (no down payment required for eligible rural properties)
Frequently Asked Questions About LTV Ratios
How Can I Lower My LTV?
You can lower your LTV ratio by making a larger down payment or by choosing a less expensive property relative to the loan amount.
Does a High LTV Affect the Mortgage Interest Rate?
Yes, a higher LTV ratio may result in higher rates because it can be seen as a higher risk for the lender. On the other hand, a lower LTV may qualify for lower rates.
What If My LTV is Above 80%?
If your LTV ratio is more than 80%, you may be required to pay mortgage insurance. This adds protection for the lender and an additional cost to the monthly mortgage payment.
Can LTV Ratios Change?
Yes, Loan-to-Value ratios can change over time as you pay down your loan and as the value of your property increases.
Understanding mortgage LTV is important to making informed decisions about your home financing. By knowing how your Loan-to-Value is calculated and its impact toward your mortgage, you can better navigate the homebuying process and know what to expect.
Our experienced and knowledgeable team at Supreme Lending is committed to helping you achieve your dream of homeownership with confidence and ease. Contact us today to learn more about your loan options and get pre-qualified today.
Related article: Mortgage DTI: What Is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
by SupremeLending | Jun 26, 2024
Understanding Down Payment Assistance Programs

When it comes to buying a home, one of the most common misunderstandings is that you need at least a 20% down payment. This misconception can discourage potential buyers, especially first-time homebuyers, from pursuing their dream of homeownership. Good news – there are several low and no down payment options, including down payment assistance programs, designed to help people become homeowners without hefty upfront costs. Discover what down payment assistance is, how it works, benefits, and other lower down payment mortgage options.
What Are Down Payment Assistance Programs?
Down payment assistance (DPA) refers to programs designed to provide financial aid to help cover part or all of the down payment and, in some cases, closing costs associated with purchasing a home. These programs can significantly reduce the upfront costs of buying a home and help more people across the country buy a home.
How Does Down Payment Assistance Work?
Down payment assistance programs are often provided by state and local governments, non-profit organizations, or other entities dedicated to promoting homeownership in local communities. DPA can come in various forms, such as grants, forgivable second loans, deferred payment loans, and tax credits. Down payment assistance programs can have specific guidelines, often targeted for first-time homebuyers and lower income areas.
- Grants. These are funds that do not need to be repaid. Essentially, they are a gift to help cover a home’s down payment.
- Forgivable Loans. When a loan is forgivable, a borrower doesn’t need to repay it after a certain time period and agreed upon criteria is met. For example, living in the primary home for a set number of years.
- Deferred Payment. This refers to loans that do not need to be repaid until the home is sold, the borrower refinances, or the mortgage is paid off.
- Tax Credits. Some down payment assistance programs offer mortgage credit certificates (MCCs) that provide a direct tax credit based on the interest paid on the loan.
Common Eligibility Requirements
While loans and down payment assistance vary by lenders and program guidelines, here’s an overview of some general eligibility criteria that may be considered.
- Income Limits. Many mortgage DPA programs have maximum income limits based on family size and location. Some lenders may consider how a borrower compares to the Area Median Income (AMI).
- Credit Score. Like most mortgages, credit score is a major factor. A minimum credit score is typically required, such as 620 for FHA and VA.
- First-time Homebuyers. Several down payment assistance programs are designed specifically for first-time homebuyers or people who haven’t owned a home within the past three years. Homebuyer education may also be included with the program as well.
- Primary Residence. In general, down payment assistance is used toward owner-occupied primary residences.
- Location. Properties may also need to be in a specific geographic area or within a targeted zone for revitalization to qualify.
- Profession. Some down payment assistance programs may also target specific occupations, such as first responders, educators, or healthcare providers. These options help give back to those who serve our communities.
Benefits of Down Payment Assistance
- Affordability. Evidently, down payment assistance can greatly reduce the amount of upfront costs when buying a home. When getting pre-qualified for a DPA program, you’ll be able to determine the right programs and potential savings.
- Increased Accessibility. Many people who might not have qualified for a traditional mortgage due to lack of savings, may qualify using down payment assistance. This helps open more doors to homeownership in your community.
- Flexibility. Down payment assistance typically can be combined with various loan types, including FHA, VA, and USDA. These typically already have lower down payment requirements to begin with. Work with an experienced, knowledgeable loan officer to discuss your options and understand what you may qualify for.
Types of Assistance
Local and State Bond Programs
Many local, regional, and state governments offer down payment assistance programs. Supreme Lending is proud to partner with these types of organizations to provide a wide range of DPA options across the country. Examples include statewide programs through the Texas State Affordable Housing Corporation (TSAHC) or California Housing Financing Agency (CalHFA), and more localized options, such as the Orange County Housing Finance Authority’s First-Time Homebuyer program.
Specialized Options
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac also have down payment assistance options, such as HomeReady® and Home Possible® that offer down payment requirements as low as 3% for Conventional loans.
Supreme Lending’s Down Payment Assistance
Through Supreme Lending’s Supreme Dream 100% financing, no-money-down program, qualified borrowers get a 30-year fixed FHA loan, followed by a fully forgivable second loan to be used toward down payment, closing costs, and pre-paids. A unique feature of this program is that no income limits are required and it can be combined with a 2-1 temporary rate buydown.
Other Low Down Payment Mortgages to Consider
- FHA loans can require down payments as low as 3.5%.
- VA loans offer qualified military Veterans 100% financing, meaning zero down payment required.
- USDA loans, guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, offer a zero down payment requirement for properties in eligible rural areas.
- Click here for an overview of common down payment requirements broken down by mortgage type.
At Supreme Lending, we’re always looking for innovative ways to help make homeownership more affordable. Whether it’s through local bond programs, low down payment loans, or our own Supreme Dream down payment assistance.
Contact us today to explore your mortgage options and down payment assistance programs.
by SupremeLending | Jun 10, 2024

When it comes to financing your new home, choosing the right mortgage is so important – FHA loans, Conventional mortgages, down payment assistance – there are several options to choose from. Each loan program has its own set of guidelines, benefits, and considerations. Comparing loan types can help you make an informed decision of what may fit your needs and homeownership goals. Let’s examine the difference between these two popular options: FHA loans and Conventional mortgages.
What Is an FHA Loan?
FHA loans are mortgages insured by the U.S. government’s Federal Housing Administration (FHA) against borrower default. They are designed to help more people who may not qualify for Conventional loans achieve homeownership. Here are some key benefits of FHA loans:
- Lower Credit Score Requirements. FHA loans typically require a minimum credit score of 580, which is lower than Conventional loans.
- Low Down Payment. One of the most attractive highlights of FHA loans is the low down payment requirement. Qualified borrowers can put down as little as 3.5% of the purchase price, plus there may be options to include down payment assistance.
- Flexible Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio. FHA loans allow higher DTI ratios, making it more feasible for borrowers with existing debt to qualify.
- Assumable Loans. FHA loans are assumable, meaning if you sell your home, the buyer can take over your existing FHA loan. This could potentially help save buyers money on closing costs and interest.
- More Lenient Qualification Requirements. In general, the qualification criteria for FHA loans is more moderate compared to Conventional loans. This helps a broader range of borrowers become homeowners.
What Are Conventional Loans?
Conventional mortgages are loans not insured or guaranteed by any government agency unlike FHA. They are offered by private lenders. Borrowers typically need to have a higher credit score and lower DTI ratio.
- Lower Mortgage Insurance Costs. While FHA requires mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) for the life of the loan, Conventional loans typically only require private mortgage insurance (PMI) until the borrower buys down 20% of the mortgage.
- Higher Loan Limits. Conventional loan borrowers can generally qualify for higher loan limits compared to FHA. This can help borrowers purchase more expensive homes.
- Variety of Loan Terms. Conventional mortgages offer a wide range of loan terms and options, including fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), providing more flexibility.
- Potential for Lower Interest Rates. Borrowers with higher credit scores and larger down payments can often secure lower interest rates with Conventional loans than FHA.
- Conforming & Non-Conforming Options. Conforming conventional loans meet the guidelines of government-sponsored enterprises (GSE), such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. While non-conforming loans do not and can have higher loan amounts, including Jumbo loans.
Frequently Asked Questions About FHA vs. Conventional Loans
Which loan is better suited for first-time homebuyers?
FHA loans are often a great option for first-time buyers due to their lower credit score and down payment options. They provide a pathway to homeownership for those who may not initially qualify for a Conventional loan.
Can I refinance* my FHA loan into a Conventional mortgage?
Yes! Borrowers can refinance an FHA loan into a Conventional one. This could potentially eliminate the FHA’s mortgage insurance requirement if you have enough equity in the home and lead to more flexible terms.
*By refinancing an existing loan, total finance charges may be higher over the life of the loan.
Are there income limits for FHA or Conventional?
FHA mortgages don’t have income limits, but they may have loan limits based on the location of the property. Conventional loans don’t have income limits either, however higher income and a better credit profile can help you qualify for a larger loan amount.
How do I decide which loan is right for me?
Take into concentration your credit score, funds you have for down payment and closing costs, and long-term goals. FHA can be ideal for those with lower credit scores, while Conventional loans may be better suited for borrowers with stronger credit profiles. Getting pre-qualified with Supreme Lending can help give you estimated costs for each option.
Whether you opt for an FHA loan or a Conventional, both options provide pathways to owning your dream home. It’s important to review your current situation, consider the benefits of different loan types, and work with a knowledgeable loan officer to help guide you through the mortgage process.
At Supreme Lending, we’re committed to helping you navigate the homebuying process with ease. Contact your local branch to get started today!







